Your Ultimate Q&A on Power Bus Systems
What is a decentralized power bus system?
A decentralized power bus system typically refers to an electrical power distribution system that is designed to manage electrical power in a decentralized or distributed manner over multiple points. In a decentralized power bus system, the power distribution is streamlined, and power is supplied closer to the point of use.
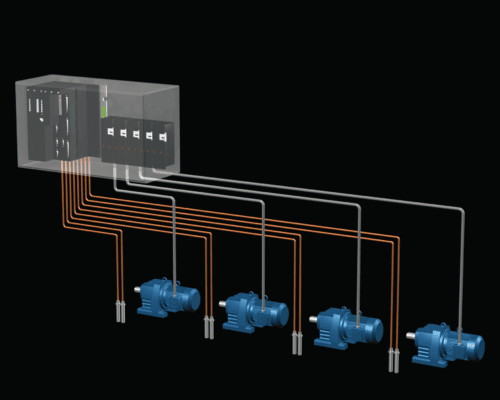
Figure 1 A typical centralized power system
How does a decentralized power bus system differ from a centralized one?
In traditional power distribution systems, power is often centralized and transmitted over long distances from power supply cabinets to various machines or motor drives. Decentralized power distribution significantly simplifies the power pathway by reducing the physical distance between a piece of equipment and its power source.
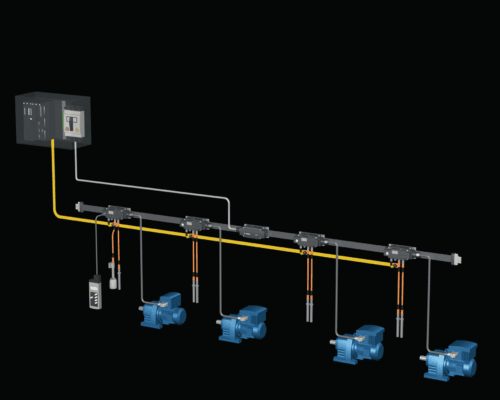
Figure 2 A Decentralized system using podis
What are the key components of a decentralized power bus system?
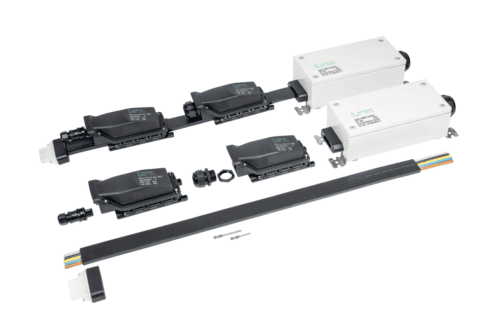
Two key components of a decentralized power distribution system are a multi-wire main power bus cable and tap-off modules. The tap-off modules are designed to connect and draw power from the bus cable to individual devices, such as motors on a conveyor line.
Depending on the system and application scenario, the incoming power could come by one of the taps or through an incomer box.
Figure 3 Components of the podis power bus
What advantages does a decentralized power bus system offer?
A decentralized power bus system offers multiple advantages to modern factories. Firstly, it significantly simplifies the design and fabrication of power infrastructure within factories and warehouses that use large conveying systems or machine cells. Significant cost reductions are achieved by minimizing complex wiring and associated electrical conduits throughout the factory or warehouse.
A decentralized power distribution system using a power bus also adds flexibility to power infrastructure by allowing motors and machinery to be connected and disconnected anywhere along the bus quickly and easily. This allows factories to effortlessly and rapidly adapt by shortening commission time.
Lastly, and unique to the podis® system, is the considerably accelerated installation time. The unique taps take only minutes to install, saving valuable time during deployment and subsequent changes.
Are there any disadvantages or challenges associated with decentralized power systems?
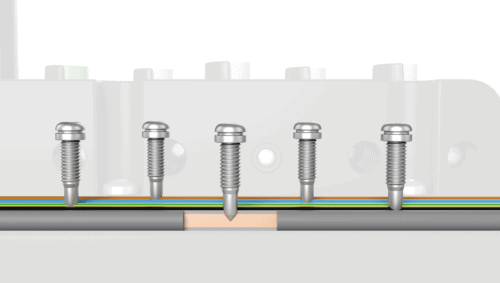
Some decentralized systems use an insulation piercing technology (IPT) which can be destructive to the copper conductor of the main power cable, resulting in voltage drop and deterioration of the system over time. However, newer technologies such as the podis® power bus use a non-damaging copper displacement technology which prolongs the system’s performance and lifespan.
Figure 5 Copper Displacement
What applications are best suited for decentralized power bus systems?
Applications such as large conveyor systems used in airport baggage handling or warehouse automation are perfect applications for decentralized power bus systems. In addition, automated machining centers and material handling equipment also work well with decentralized power.
How are faults managed in a decentralized power bus system?
Managing faults in a decentralized power bus system involves a combination of protective measures, monitoring, and control strategies to ensure the reliability and safety of the system. Integrated circuit breakers or fuses, current monitoring sensors at the start of a power bus or temperature sensors placed on equipment or motors may all be integrated into a decentralized bus system.
What standards exist for decentralized power bus systems?
In the US, standards such as UL 2875 (Signal and Power Distribution for Industrial Control) and UL 1277 (Standard for Electrical Power and Control Tray Cables) dictate the use of power bus distribution systems.